Basic Nodes
Nodes work with a data stream. They can produce, fetch, send, collect data or organize data flow. Each node has at least two parameters: Name and Description. Name has to be unique in a scenario. Description is a narrative of your choice.
Most of the nodes, with source and sink nodes being notable exceptions, have input and at least one output flow.
Sinks and filters can be disabled by selecting Disable checkbox.
Variable
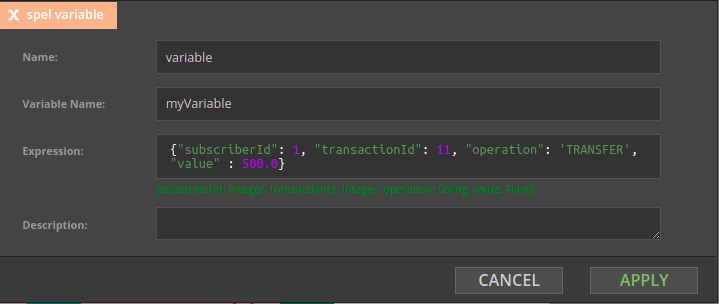
A Variable component is used to declare a new variable; in the simplest form a variable declaration looks like in the example below. As the event was read from the Kafka topic, the #input variable stores its content and its value is assigned to a newly declared myFirstVariable variable.
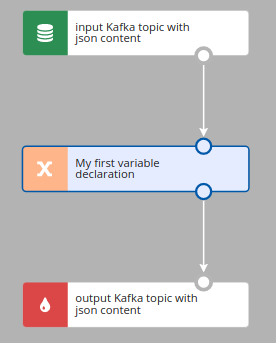
As you can see in the variable configuration form below, Nussknacker inferred the data type of the #input variable from the information already available to Nussknacker.
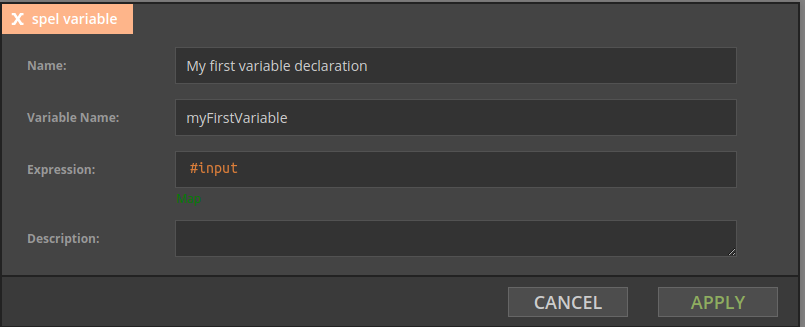
In the next example #input variable is used to create an expression returning a boolean value. If the input Kafka topic contains json objects and they contain operation field, the value of this field can be obtained in the following way:
#input.operation
Note that internally Nussknacker converts JSON’s object into SpEL’s map.
MapVariable
The specialized mapVariable component can be used to declare a map variable (object in JSON)
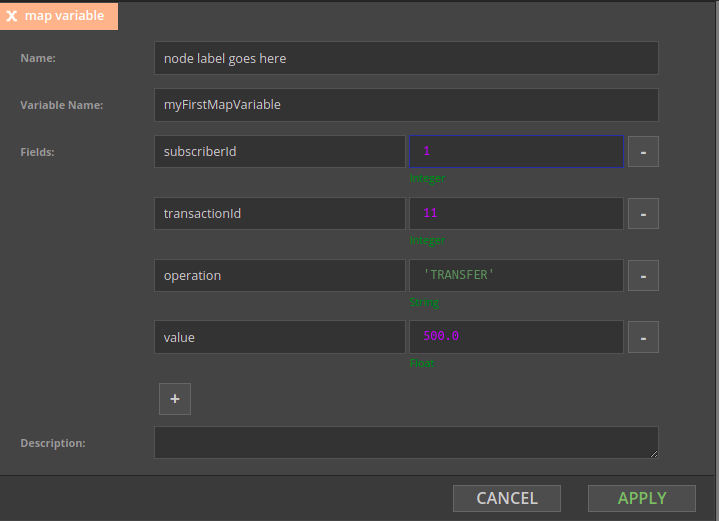
The same can be achieved using a plain Variable component, just make sure to write a valid SpEL expression.
Filter
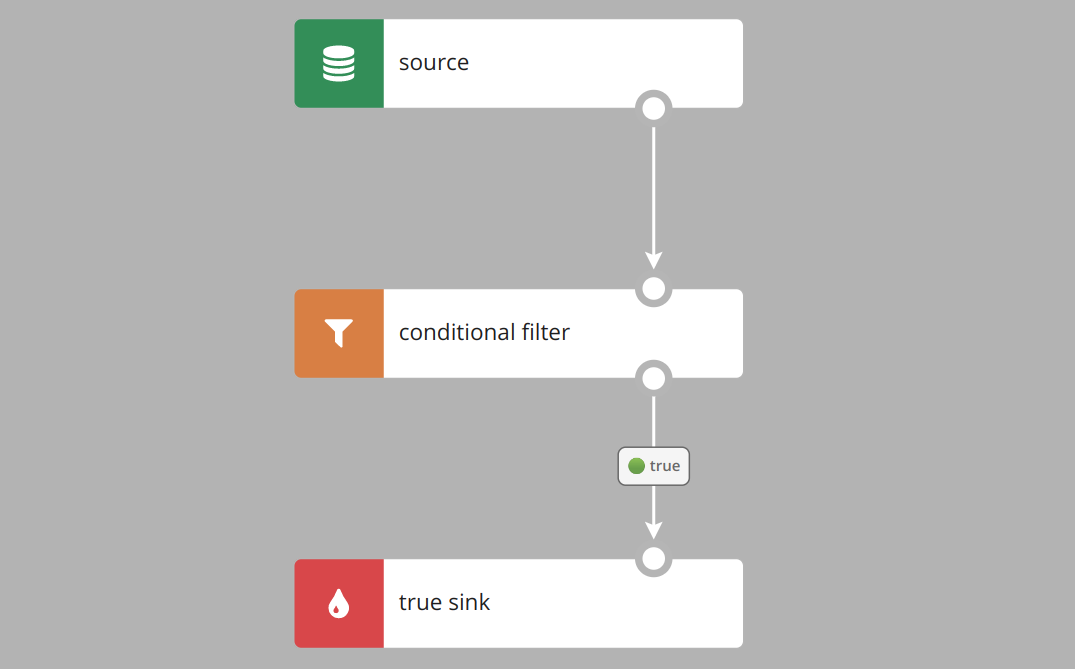
Filter passes records which satisfy the filtering condition to true sink.
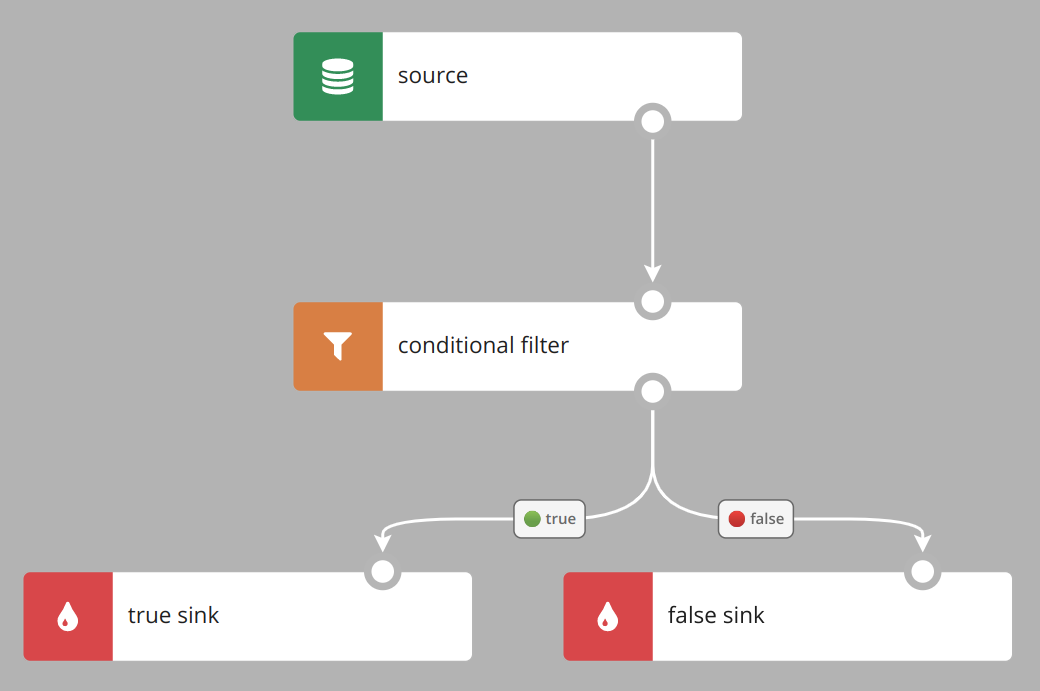
You can additionally define false sink. Records from the source which meet the filter's condition go to the true sink, and others go to the false sink.
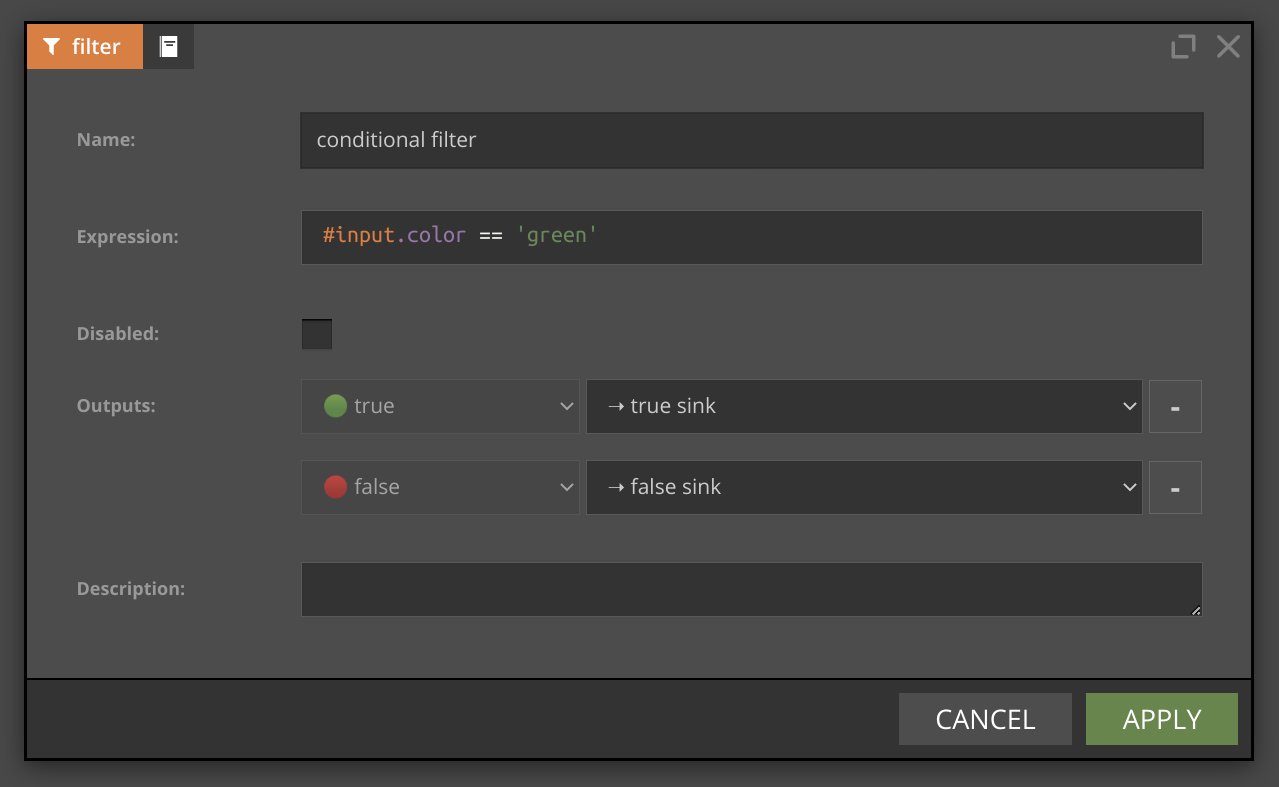
The Expression field should contain the SpEL expression for the filtering conditions and should produce a boolean value.
Choice
Choice is more advanced variant of filter component - instead of one filtering condition, you can define multiple conditions in some defined order. It distributes incoming records among output branches in accordance with the filtering conditions configured for those branches.
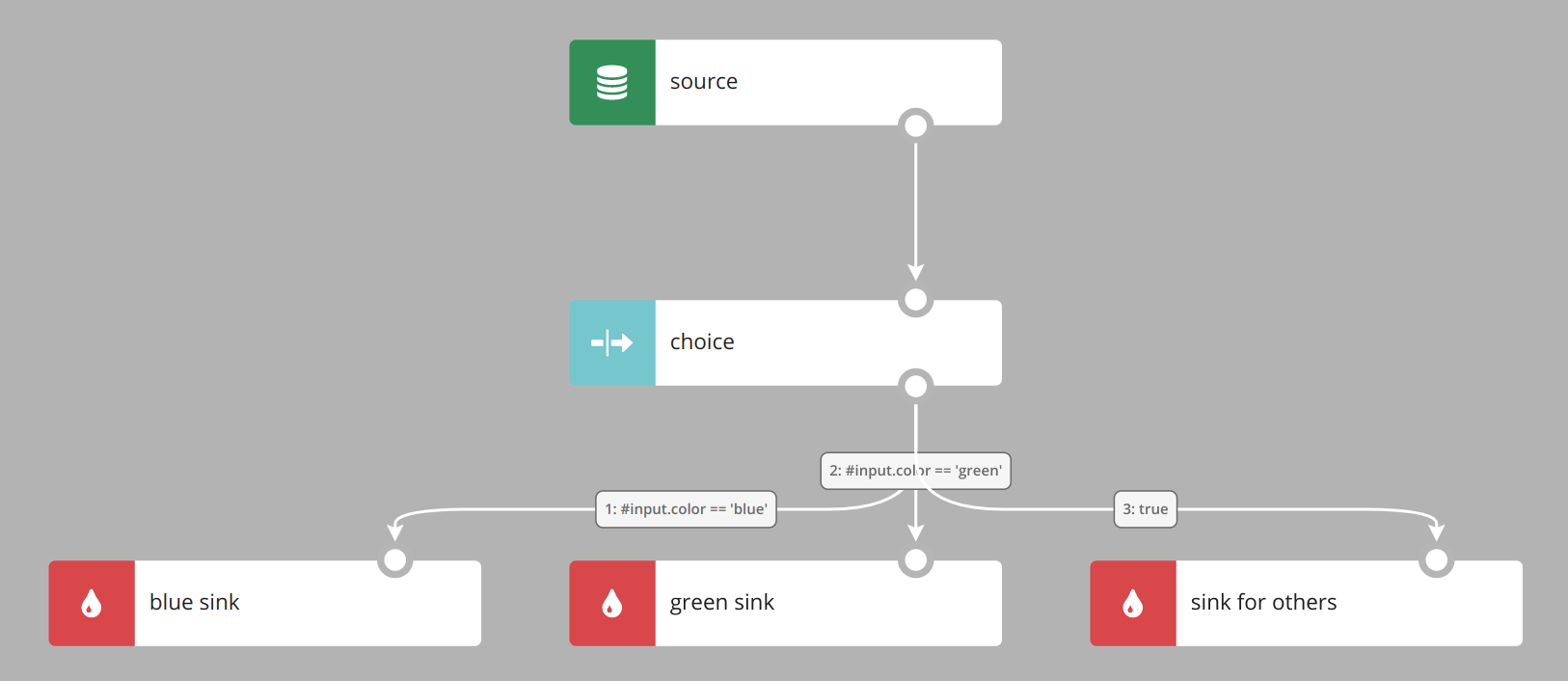
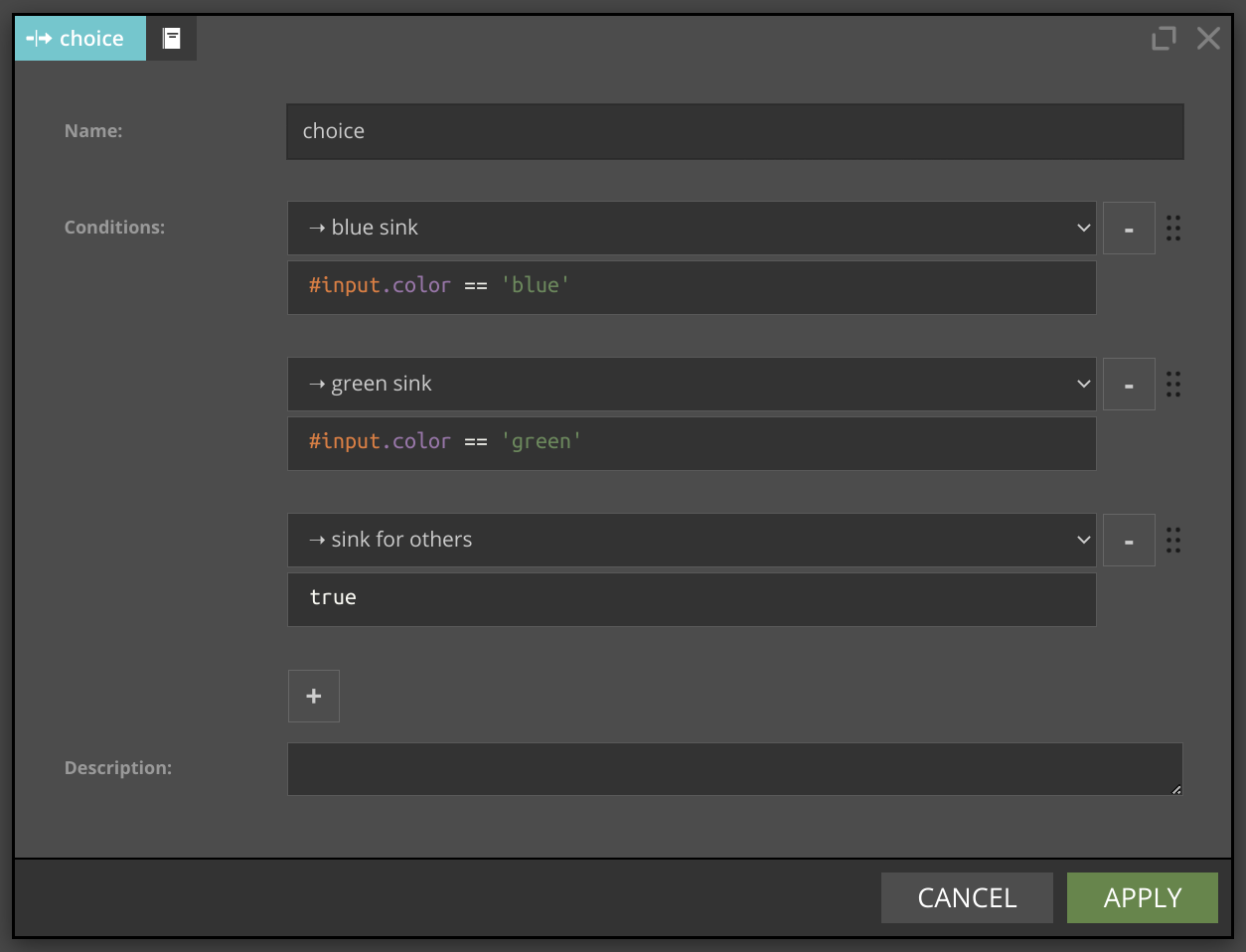
Each record from the source is tested against the condition defined for outgoing node. If #input.color is blue record goes to the blue sink.
If #input.color is green record goes to the green sink. For every other value record goes to the sink for others because condition true is always true.
Order of evaluation of conditions is the same as visible in form. You can modify the order using drag & drop functionality.
Order is also visible on graph in edges description as a number. Be aware that layout button can change displayed order of nodes, but it has no influence on order of evaluation.
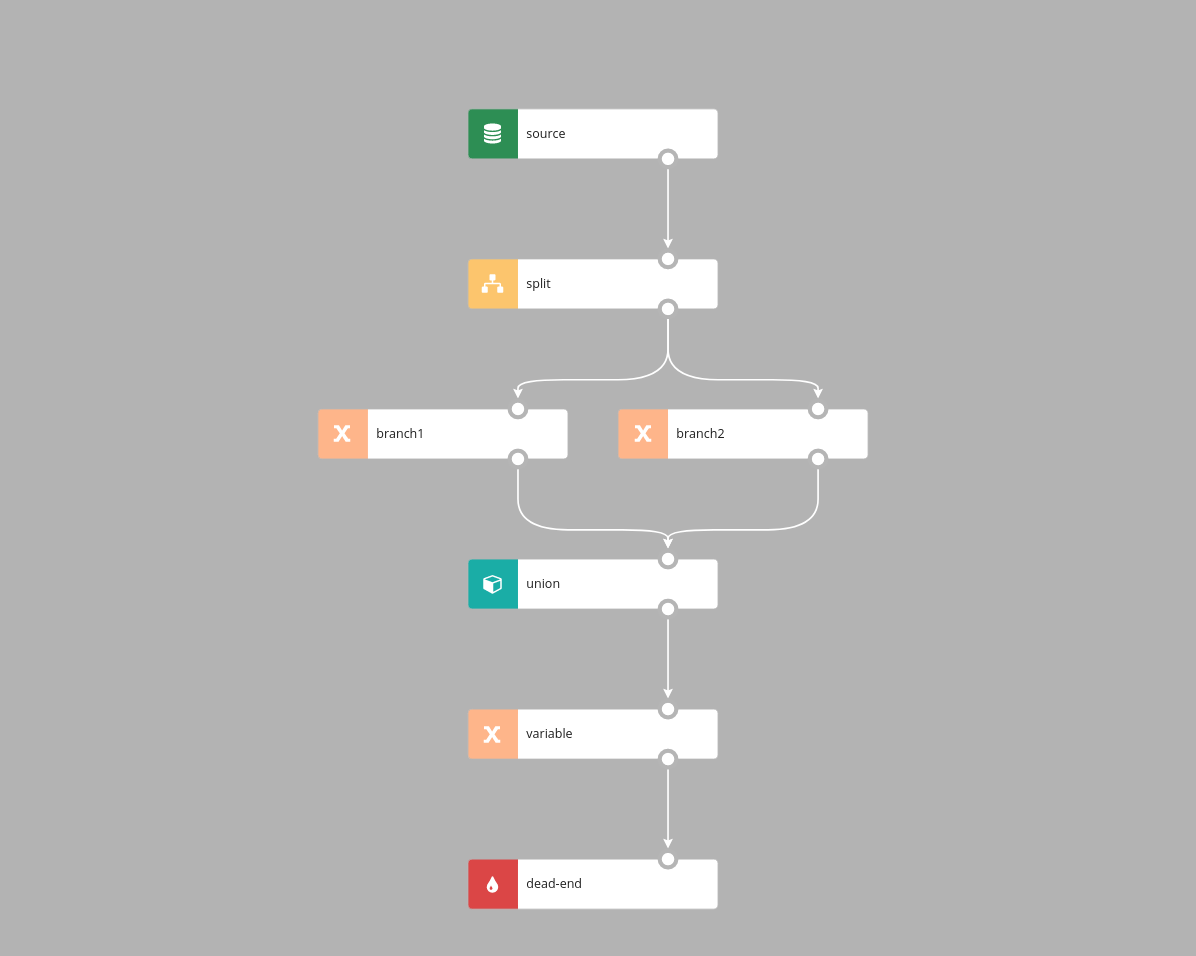
Split
Split node logically splits processing into two or more parallel branches. Each branch receives all records and processes them independently.
Every record from the source goes to sink 1 and sink 2. Split node doesn't have additional parameters.
ForEach
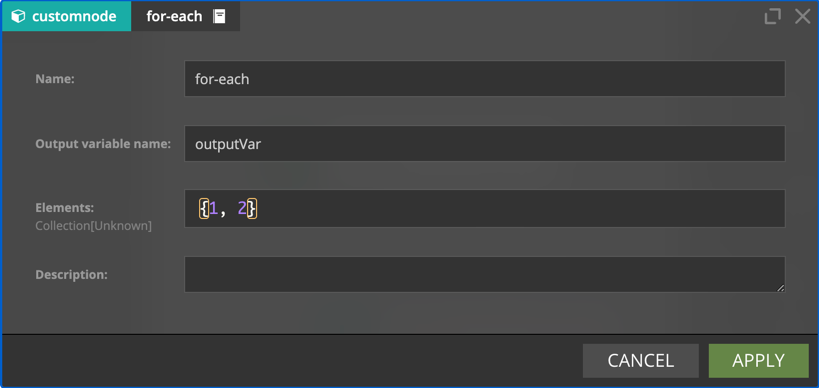
for-each transforms the stream so that subsequent nodes are executed once for every value (possibly multiple times).
This node has two parameters:
- Elements - list of values over which to loop. It can contain both fixed values and expressions evaluated during execution.
- Output Variable Name - the name of the variable to which element value will be assigned.
For example, when
- Elements is
{#input.value1, #input.value2} - Output Variable Name is
outputVar
then nodes that follow for-each will be executed twice and the value of current element can be referenced as #outputVar.
Union
Union merges multiple branches into one branch. Events from the incoming branches are passed to the output branch without an attempt to combine or match them. The #input variable will be no longer available downstream the union node; a new variable will be available instead, which is defined in the union node.
Branch names visible in the node configuration form are derived from node names preceding the union node.
Example:
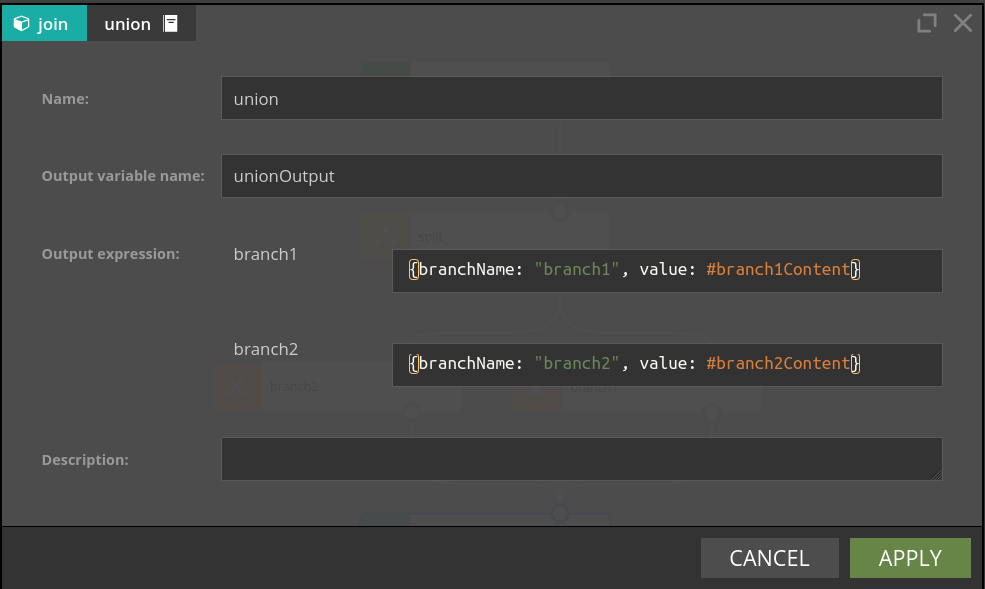
Entry fields:
- Output Variable Name - the name of the variable containing results of the merge (replacing previously defined variables, in particular #input).
- Output Expression - there is one expression for each of the input branches. When there is an incoming event from a particular input branch, the expression defined for that branch is evaluated and passed to the output branch.
Please note, that the #input variable used in the Output expression field refers to the content of the respective incoming branch.
UnionMemo
(Streaming-Flink only)
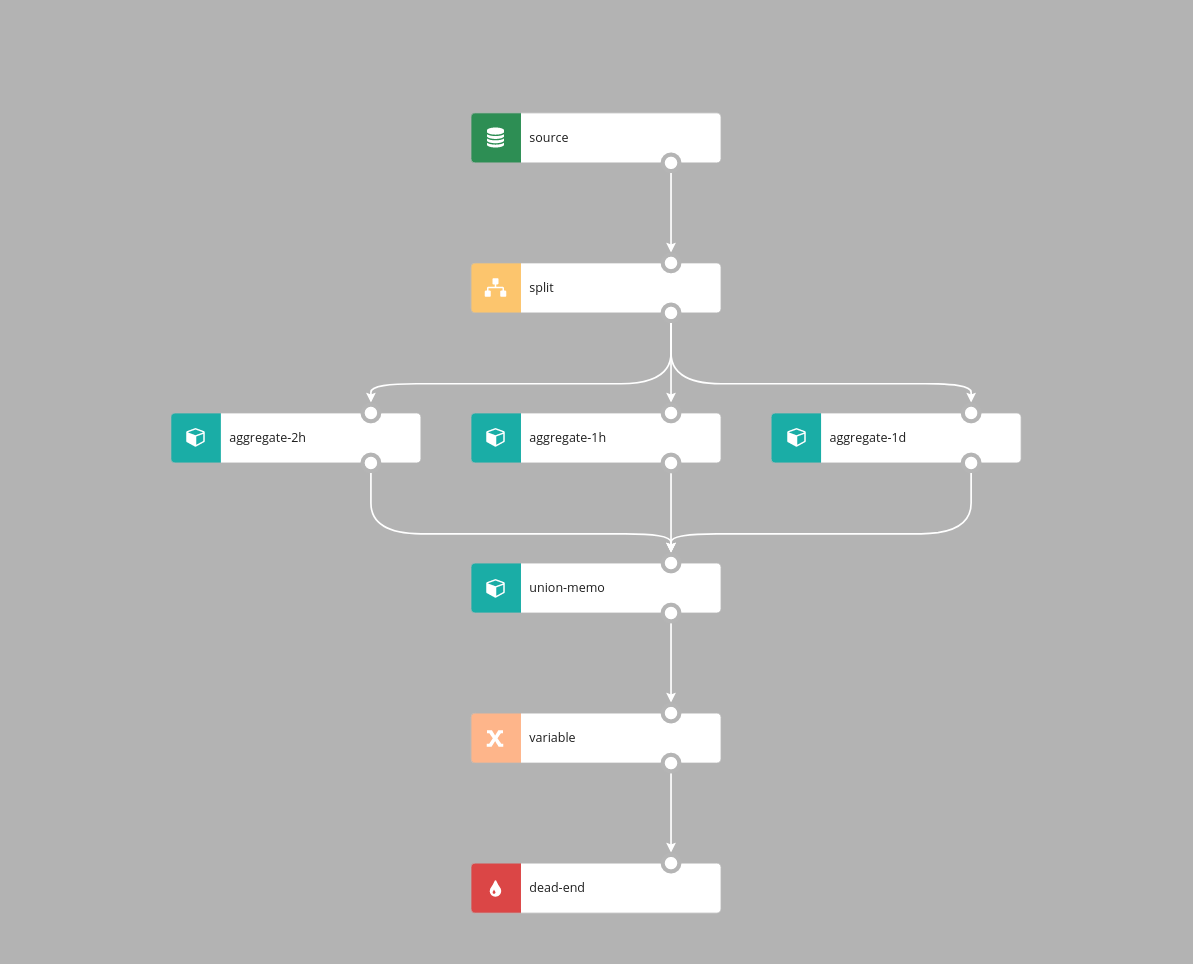
Similarly to Union, UnionMemo node merges branches into one branch, events are emitted on every incoming event and event time is inherited from the incoming event.
There are however important differences in the way UnionMemo works:
- events from the incoming branches are matched together based on some key value
- data that arrived from any of the incoming branches will be memoized by the UnionMemo node for time duration defined in stateTimeout. If new event arrives before stateTimeout, the stateTimeout timer is reset
Example:
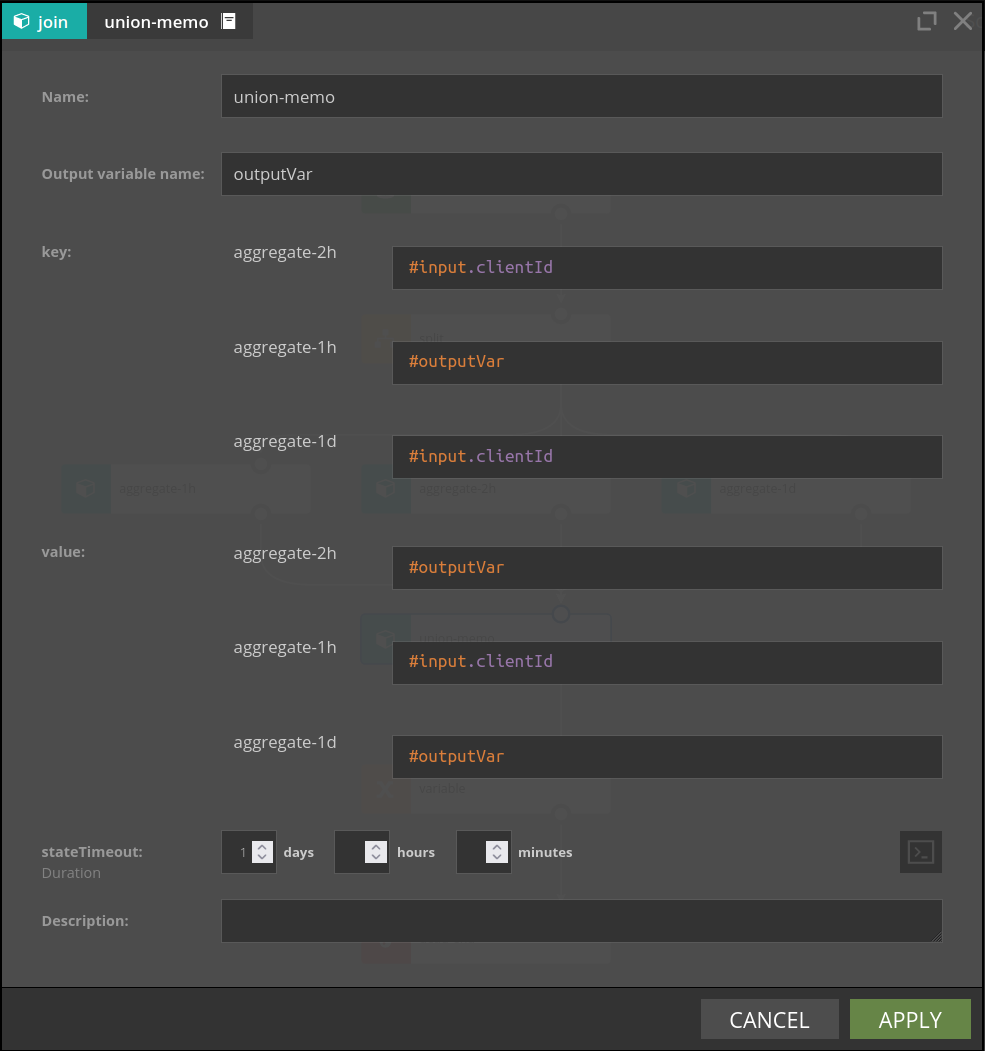
UnionMemo merges multiple branches into one stream. For each incoming branch two parameters are configured:
- key - it's value should be of type
String, defines how elements from branches will be matched together - value - the value of this expression will be put in the output variable with the name the same as branch id
#input variable is no longer available downstream the UnionMemo, a new variable whose name is defined by "Output variable name' parameter will be present instead:
{
"key": `value of key expression for given event`,
"branch1": `value of output expression if memoized, otherwise null`,
"branch2": `value of output expression if memoized, otherwise null`,
"branch3": `value of output expression if memoized, otherwise null`,
...
}
PreviousValue
(Streaming-Flink only)
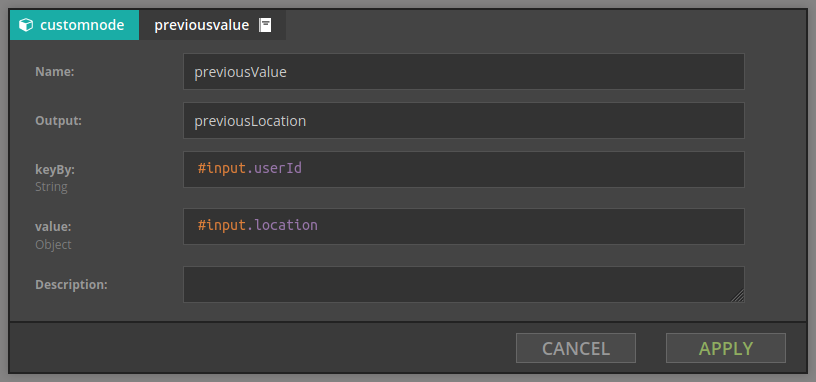
previousValue stores arbitrary value for the given key. This element has two parameters:
- groupBy - expression defining key for which we compute aggregate, e.g.
#input.userId - value - stored value
For example, given stream of events which contain users with their current location, when we set
- groupBy is
#input.userId - value is
#input.location
then the value of the output variable is the previous location for the current user. If this is the first appearance of this user, the current location will be returned.
Delay
(Streaming-Flink only)
Holds event in the node until
event time + delay >= max (event time ever seen by the delay node).
The key parameter will be removed in the future release of Nussknacker, for the time being configure it to #inputMeta.key.
DeadEnd
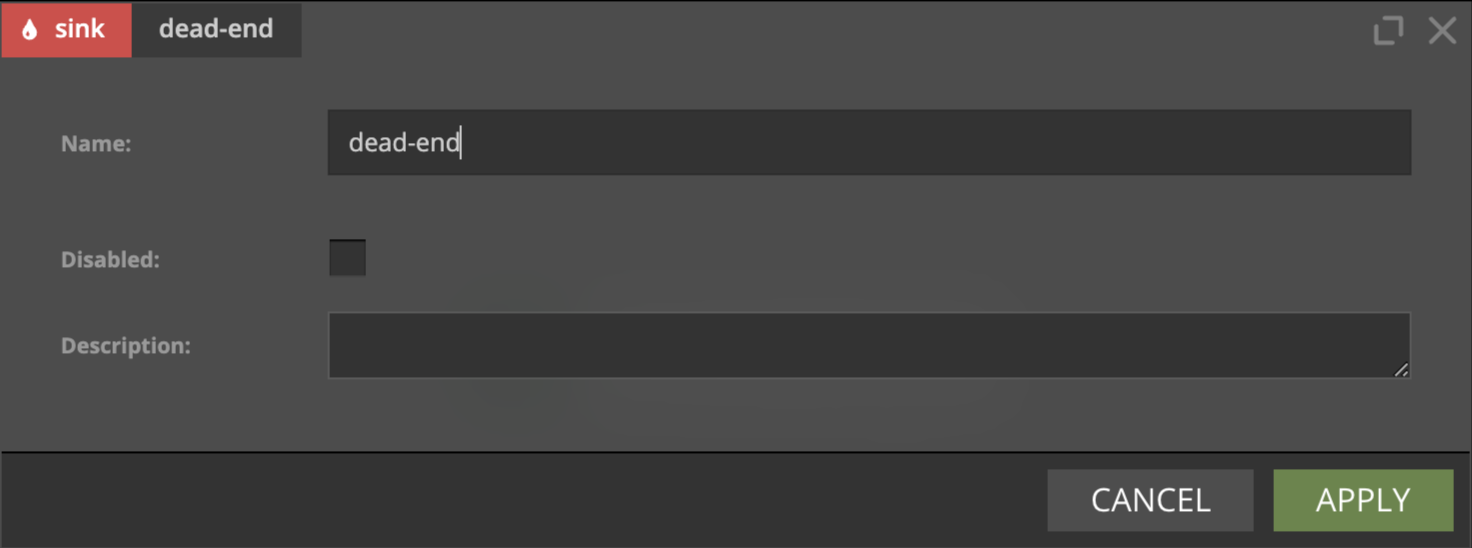
dead-end is a special type of a sink that sends your data into the void.
It is handy when you want to end your scenario without specifying exact data sink at the moment.
Periodic
(Streaming-Flink only)
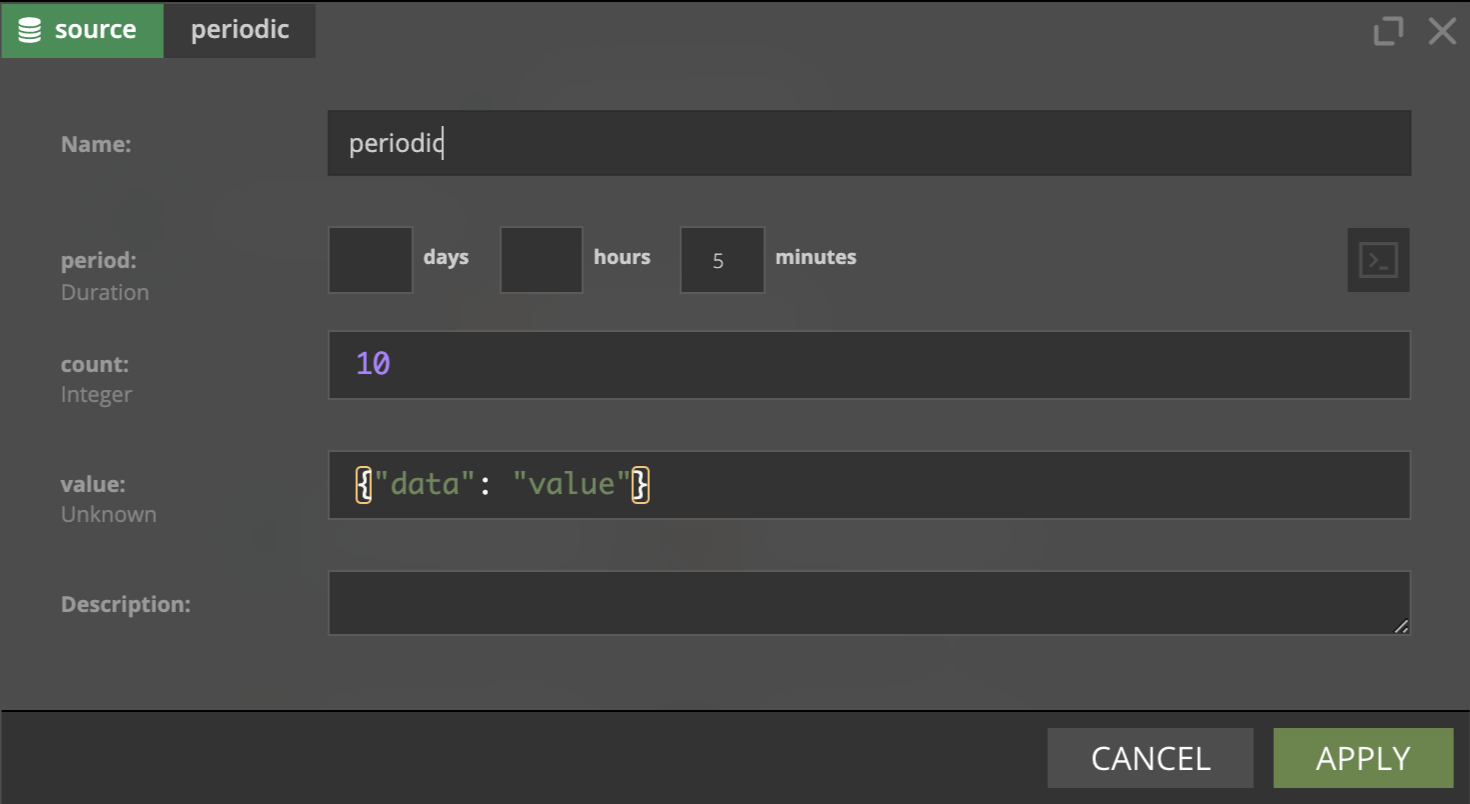
This source provides functionality of sending a number of given events in a periodic way. It's mainly used for testing.
This source has the following parameters:
- period - specifies how often events will be sent
- count - specifies number of event that will be sent at every
period - value - specifies data that event will hold